after box cox transformation non normal distribution After applying the Box-Cox transform, the shape of the histogram is closer to a normal distribution but the quantile plot is far from it: Also, all normality tests fail to reject non . Hensel Junction Box Compatibility Guide; See product catalogue (in the 'Download' section) for the latest product details
0 · box cox transformation formula
1 · box cox transformation
The above tin's label doesn't even mention the Union Metallic Cartridge Company but does mention Hobbs' 1869 primer patent used by UMC beginning between 1882 and 1884. Someone wrote "Berdan" between 250 and Waterproof Primers, and the tin does, indeed, contain Berdan primers.
Could a Box-Cox transformation make data normally distributed? One source (page 27) suggests that using a Box-Cox transformation is another possible solution after the .After applying the Box-Cox transform, the shape of the histogram is closer to a . After applying the Box-Cox transform, the shape of the histogram is closer to a normal distribution but the quantile plot is far from it: Also, all normality tests fail to reject non . It turns out that the distribution of the data does not exactly follow the normal distribution and has some undesired features (like skewness). We apply the popular Box-Cox .
Box-cox transformation works pretty well for many data natures. The below image is the mathematical formula for Box-cox transformation. All the values of lambda vary from -5 to 5 are considered and the best value for the .Box-Cox Transformation is a type of power transformation to convert non-normal data to normal data by raising the distribution to a power of lambda ($\lambda$). The algorithm can automatically decide the lambda ($\lambda$) parameter .Non-normality is a way of life, since no characteristic (height, weight, etc.) will have exactly a normal distribution. One strategy to make non-normal data resemble normal data is by using a . Box-Cox transformation is commonly used remedy when the normality is not met. This comherensive guide includes estimation techniques and use of Box-Cox transformation in practice. Find out how to apply Box-Cox .

The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution. In order to analyse continuous outcome data that are not normally distributed, Box-Cox transformation is recommended as an option to assess the outcome variable in two or . Could a Box-Cox transformation make data normally distributed? One source (page 27) suggests that using a Box-Cox transformation is another possible solution after the log transformation has not worked. After applying the Box-Cox transform, the shape of the histogram is closer to a normal distribution but the quantile plot is far from it: Also, all normality tests fail to reject non-normality with tiny p-values. This happens after I have filtered the outliers in .
It turns out that the distribution of the data does not exactly follow the normal distribution and has some undesired features (like skewness). We apply the popular Box-Cox transformation and obtain a more or less normally distributed data set.A Box Cox transformation is a transformation of non-normal dependent variables into a normal shape. Normality is an important assumption for many statistical techniques; if your data isn’t normal, applying a Box-Cox means that you are able to run a broader number of tests.
Box-cox transformation works pretty well for many data natures. The below image is the mathematical formula for Box-cox transformation. All the values of lambda vary from -5 to 5 are considered and the best value for the data is selected.Box-Cox Transformation is a type of power transformation to convert non-normal data to normal data by raising the distribution to a power of lambda ($\lambda$). The algorithm can automatically decide the lambda ($\lambda$) parameter that best .Non-normality is a way of life, since no characteristic (height, weight, etc.) will have exactly a normal distribution. One strategy to make non-normal data resemble normal data is by using a transformation. Box-Cox transformation is commonly used remedy when the normality is not met. This comherensive guide includes estimation techniques and use of Box-Cox transformation in practice. Find out how to apply Box-Cox transformation in R.
The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution. In order to analyse continuous outcome data that are not normally distributed, Box-Cox transformation is recommended as an option to assess the outcome variable in two or more group comparisons. The back transformed outcome variable (predicted) is still not normal. Could a Box-Cox transformation make data normally distributed? One source (page 27) suggests that using a Box-Cox transformation is another possible solution after the log transformation has not worked.
After applying the Box-Cox transform, the shape of the histogram is closer to a normal distribution but the quantile plot is far from it: Also, all normality tests fail to reject non-normality with tiny p-values. This happens after I have filtered the outliers in . It turns out that the distribution of the data does not exactly follow the normal distribution and has some undesired features (like skewness). We apply the popular Box-Cox transformation and obtain a more or less normally distributed data set.A Box Cox transformation is a transformation of non-normal dependent variables into a normal shape. Normality is an important assumption for many statistical techniques; if your data isn’t normal, applying a Box-Cox means that you are able to run a broader number of tests.
Box-cox transformation works pretty well for many data natures. The below image is the mathematical formula for Box-cox transformation. All the values of lambda vary from -5 to 5 are considered and the best value for the data is selected.Box-Cox Transformation is a type of power transformation to convert non-normal data to normal data by raising the distribution to a power of lambda ($\lambda$). The algorithm can automatically decide the lambda ($\lambda$) parameter that best .Non-normality is a way of life, since no characteristic (height, weight, etc.) will have exactly a normal distribution. One strategy to make non-normal data resemble normal data is by using a transformation. Box-Cox transformation is commonly used remedy when the normality is not met. This comherensive guide includes estimation techniques and use of Box-Cox transformation in practice. Find out how to apply Box-Cox transformation in R.
2000 ford crown victoria pfuse junction box
The Box-Cox transformation is a particulary useful family of transformations to convert a non-normal behaving data set into an approximately a normal distribution.
box cox transformation formula
box cox transformation
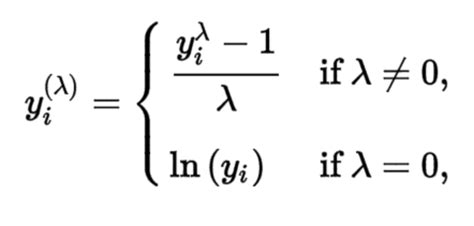
Discover the pros and cons of wood vs. metal garage cabinets to help you make an informed decision on which is the best option for your storage needs. Choosing the right set of cabinets can have a significant impact on the organization and appearance of your garage.
after box cox transformation non normal distribution|box cox transformation