a removable partial denture cast metal framework is fabricated (1) Introduction: This review aimed to synthesize the significant literature addressing digital techniques for producing removable partial denture (RPD) metal frameworks, focusing on oral fit outcomes. Luminaires recessed in ceilings, floors, or walls shall not be used to access outlet, pull, or junction boxes or conduit bodies, unless the box or conduit body is an integral part of the listed luminaire'
0 · titanium dentures photos
1 · removable partial denture cast metal
2 · partial with metal clasps
3 · partial dentures without metal clasps
4 · partial cast metal with resin
5 · mandibular partial denture cast metal
6 · clear framework for partial dentures
7 · cast metal partial dentures images
Depending on the pattern and type of sheet metal, you can use several different kinds of equipment to make a cut. You can use an electric saw for simple lines, or you can try tin snips, dremels, or metal nibblers for complex designs with curved lines.
3D printed polyamide (Valplast) removable partial denture. The prosthesis lacks rest seats and clasp assemblies and relies on engaging retentive undercuts of the remaining teeth. An overview.Manufacturing methods for the metal frameworks of removable partial dentures (RPDs) have recently transitioned from conventional lost-wax techniques to computer-aided design (CAD) .
This article describes a combined conventional and digital workflow for fabricating removable partial dentures (RPDs). After scanning the dental cast and RPD framework . (1) Introduction: This review aimed to synthesize the significant literature addressing digital techniques for producing removable partial denture (RPD) metal frameworks, focusing on oral fit outcomes.
Cast metal removable partial dentures, fabricated from different alloys, have been used to treat the partially edentulous patient for decades. Although initially made from alloys of type IV gold, cobalt and nickel chromium .However, fabrication of removable partial dentures (RPDs) using computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing is limited by its technique sensitivity as the pink resin, which . This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to investigate the accuracy of removable partial denture (RPD) frameworks fabricated by computer-aided design/ computer . Influence of reinforcement bar on accuracy of removable partial denture framework fabricated by casting with a 3D-printed pattern and selective laser sintering
Rapid advancements in computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) have opened new pathways in the fabrication of removable partial dentures (RPDs) through additive and subtractive processes.
For the medium palatal vault casts, Co-Cr frameworks of the conventional casting (CON) group (n=5) were fabricated with the lost wax technique. For the 3D printing pattern casting (PPC) group (n=5), wax patterns of the framework .
3D printed polyamide (Valplast) removable partial denture. The prosthesis lacks rest seats and clasp assemblies and relies on engaging retentive undercuts of the remaining teeth. An overview.Manufacturing methods for the metal frameworks of removable partial dentures (RPDs) have recently transitioned from conventional lost-wax techniques to computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) techniques, specifically metal . This article describes a combined conventional and digital workflow for fabricating removable partial dentures (RPDs). After scanning the dental cast and RPD framework assembly, artificial teeth and denture base regions were designed using computer-aided design software. (1) Introduction: This review aimed to synthesize the significant literature addressing digital techniques for producing removable partial denture (RPD) metal frameworks, focusing on oral fit outcomes.
Cast metal removable partial dentures, fabricated from different alloys, have been used to treat the partially edentulous patient for decades. Although initially made from alloys of type IV gold, cobalt and nickel chromium alloys have been used for the fabrication of cast frameworks since the 1930s [7, 8].However, fabrication of removable partial dentures (RPDs) using computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing is limited by its technique sensitivity as the pink resin, which encases part of metal framework, cannot be fabricated digitally. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to investigate the accuracy of removable partial denture (RPD) frameworks fabricated by computer-aided design/ computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems compared to frameworks produced by conventional casting methods. Influence of reinforcement bar on accuracy of removable partial denture framework fabricated by casting with a 3D-printed pattern and selective laser sintering
Rapid advancements in computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) have opened new pathways in the fabrication of removable partial dentures (RPDs) through additive and subtractive processes.For the medium palatal vault casts, Co-Cr frameworks of the conventional casting (CON) group (n=5) were fabricated with the lost wax technique. For the 3D printing pattern casting (PPC) group (n=5), wax patterns of the framework were printed, followed by metal casting. 3D printed polyamide (Valplast) removable partial denture. The prosthesis lacks rest seats and clasp assemblies and relies on engaging retentive undercuts of the remaining teeth. An overview.
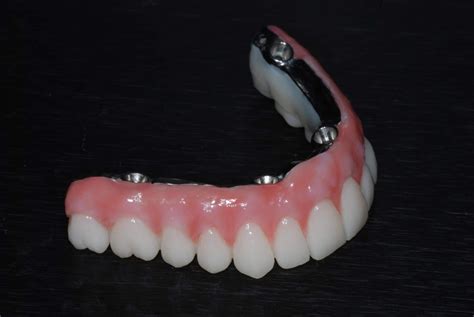
Manufacturing methods for the metal frameworks of removable partial dentures (RPDs) have recently transitioned from conventional lost-wax techniques to computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) techniques, specifically metal . This article describes a combined conventional and digital workflow for fabricating removable partial dentures (RPDs). After scanning the dental cast and RPD framework assembly, artificial teeth and denture base regions were designed using computer-aided design software. (1) Introduction: This review aimed to synthesize the significant literature addressing digital techniques for producing removable partial denture (RPD) metal frameworks, focusing on oral fit outcomes.
Cast metal removable partial dentures, fabricated from different alloys, have been used to treat the partially edentulous patient for decades. Although initially made from alloys of type IV gold, cobalt and nickel chromium alloys have been used for the fabrication of cast frameworks since the 1930s [7, 8].However, fabrication of removable partial dentures (RPDs) using computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing is limited by its technique sensitivity as the pink resin, which encases part of metal framework, cannot be fabricated digitally.
titanium dentures photos
removable partial denture cast metal
This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to investigate the accuracy of removable partial denture (RPD) frameworks fabricated by computer-aided design/ computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) systems compared to frameworks produced by conventional casting methods.
Influence of reinforcement bar on accuracy of removable partial denture framework fabricated by casting with a 3D-printed pattern and selective laser sintering Rapid advancements in computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) have opened new pathways in the fabrication of removable partial dentures (RPDs) through additive and subtractive processes.

partial with metal clasps
partial dentures without metal clasps
partial cast metal with resin

Sheet metal fabrication is a process of working with metal, used in various industries, ranging from construction and automotive to warehouse and electronics. It involves transforming flat sheets of metal into functional components and structures through cutting, .
a removable partial denture cast metal framework is fabricated|partial cast metal with resin