shape of distribution box plots What is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot . IP65 Waterproof: The project box is IP65 Waterproof certificated, can protect against dust, corrosion and splashing water, ensure electrical components dry and effective in harsh environments.
0 · symmetric box and whisker plot
1 · skewness on a box plot
2 · skewed box and whisker plot
3 · shape of distribution skewed right
4 · shape of distribution skewed left
5 · right skewed data box plot
6 · right skewed box plot vertical
7 · explain box plot with example
$9.88
Compare the respective medians of each box plot. If the median line of a box plot lies outside of the box of a comparison box plot, then there is likely to be a difference between the two groups. Source: https://blog.bioturing.com/2018/05/22/how-to-compare-box-plots/ See more
Compare the interquartile ranges (that is, the box lengths) to examine how the data is dispersed between each sample. The longer the box, the . See moreWhen reviewing a box plot, an outlier is defined as a data point that is located outside the whiskers of the box plot. See moreWhat is a Box Plot? A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot .Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
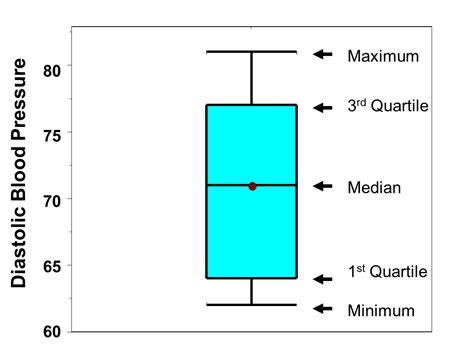
Box plots are useful because they allow us to gain a quick understanding of the distribution of values in a dataset. They’re also useful for comparing two different datasets. When comparing two or more box plots, we . A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], .
The term “box plot” refers to an outlier box plot; this plot is also called a box-and-whisker plot or a Tukey box plot. See the "Comparing outlier and quantile box plots" section below for another type of box plot. Here are the .
Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median .A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with . A box plot is a type of plot that displays the five number summary of a dataset, which includes: The minimum value; The first quartile (the 25th percentile) . Conversely, the line in the middle of the box plot for Study .
Distribution shape refers to the visual representation of how data points are spread across different values in a dataset. It describes the overall appearance of the data when plotted, showing features like symmetry, skewness, peaks, and tails. Understanding distribution shape is essential for interpreting data in various formats, including box plots, histograms, stem-and .Shapes of Box-and-Whisker Plots . Most data on the left A box-and-whisker plot also shows the shape of a distribution. Section 10.4 Box-and-Whisker Plots 463 9 +(- 6 )= 3 3 +(- 3 )= 4 +(- 9 )= 9 +(- 1 )= 4. The box-and-whisker plots represent the daily attendance at two beaches during July. Compare and contrast the attendances for the two . Box plots, also called box and whisker plots, are more useful than histograms for comparing distributions. . The shape of this distribution is described better with more intervals than we had . For a scalar random variable, the following plots are all useful depictions of the distribution: The box plot: This is a simple plot that shows various quantiles of the data using a standard box-and-whiskers method, as well as showing "outliers" that are outside some multiple of the interquartile range. This plot gives a simple sense of where the bulk of the data lies, via .
Interpreting a Box Plot can reveal crucial insights into your data distribution. Box Plots are a powerful visual tool for understanding central tendencies, variations, and potential anomalies. By examining the various elements of a Box Plot, such as the median, quartiles, and whiskers, you can quickly assess the spread and shape of your dataset . Box Plot is a graphical method to visualize data distribution for gaining insights and making informed decisions. Box plot is a type of chart that depicts a group of numerical data through their quartiles. . Information that are missed in a box plot is the detailed shape of the distribution. It is quite difficult to find the mean as it is .The histogram and the box plot both group data together. Since histograms and box plots do not display each data value individually, they do not provide information about the shape of the distribution to the same level of detail that a dot plot does. This distribution, in particular, can also be called bell-shaped. These box plots show the basketball scores for two teams. Bulldogs 55 70 80 90 105 Wolverines 35 55 80 85 96 Basketball scores Compare the shapes of the box plots. A. The Bulldogs' distribution is symmetric, but the Wolverines' distribution is negatively skewed. B. Both distributions are symmetric. C. Both distributions are negatively skewed. D.
The following box plots display the results. a. In complete sentences, describe what the shape of each box plot implies about the distribution of the data collected. b. Have more Americans or more Germans surveyed been to over eight foreign countries? c. Compare the three box plots.The distribution is shaped like a triangle reflected by a horizontal line at 4.5. The distribution is bimodal. It is almost symmetric. The shape of the distribution is a “U” where the maximum value is more frequent than the minimum value. The distribution is shaped like a rectangle. The shape of the distribution is uniform.
The distribution shape can give you a visual which helps to show how the data is: Spread out (e.g. dispersion, variability, scatter), . A symmetric box plot. 3. Skewness. Shapes of distributions can differ in skewness; these distributions are not symmetrical distributions. Instead, they have more points plotted on one side of the mean than on . A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.” Here’s an example. Different parts of a boxplot | Image: Michael .We should expect then that the shape of the data would be the same whether it is represented in a curve, box plot or histogram. Remember that the shape of data can be symmetric, negatively skewed or positively skewed. For a symmetric distribution: The median is in the centre of the range and the tails (whiskers) of the data are of equal length.Solutions for Chapter 2 Problem 86P: In a survey of 20-year-olds in China, Germany, and the United States, people were asked the number of foreign countries they had visited in their lifetime. The following box plots display the .

The box plots show the distribution of times spent shopping by two different groups. Questions : 1. . Compare the shapes of the box plots. The positions and lengths of the boxes and whiskers appear to be very similar. In both plots, the right whisker is shorter than the left whisker. 2.
symmetric box and whisker plot
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A dot plot is best applied when____ A) A single variable is summarised B) The mean, median, and mode are equal C) The general shape of distribution is symmetric D) The relationship between two variables is summarised, A dot plot can be used to show ___ A) The mean, median, and mode B) The .Similar to histograms, box plots and violin plots also help describe the shape to determine dispersion within our datasets. Box plots are great tools for basic summary statistics such as finding IQR, skew, outliers, etc. However, we do not actually see the dispersion in the data.
Effective data distribution visualization: Box plots are particularly useful for visualizing asymmetric or irregularly shaped data distributions. . spread, and shape of the data 20. Box plots are great for comparing data across different groups. They help in exploring data and sharing results 20 21. This makes them a big help in data analysis . A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew. Box plots are good at portraying extreme values and are especially good at showing differences between distributions. However, many of the details of a distribution are not revealed in a box plot; to examine these details one should create a histogram and/or a stem-and-leaf display. What is a box plot? A box plot shows the distribution of data for a continuous variable. . Both box plots and histograms show the shape of your data. Both can be used to identify unusual points or outliers. Figure 3 shows an outlier box plot and a histogram for the same set of data. In this example, the histogram is vertical instead of .
It is less easy to justify a box plot when you only have one group’s distribution to plot. Box plots offer only a high-level summary of the data and lack the ability to show the details of a data distribution’s shape. With only one group, we have the freedom to choose a more detailed chart type like a histogram or a density curve.
In a symmetric distribution, the mean is equal to the median and there is a vertical line of symmetry in the center of the data display.The histogram and the box plot both group data together. Since histograms and box plots do not display each data value individually, they do not provide information about the shape of the distribution to the same level of detail that a dot plot . What is a box plot? A box plot shows the distribution of data for a continuous variable. . Both box plots and histograms show the shape of your data. Both can be used to identify unusual points or outliers. Figure 3 shows an outlier box plot and a histogram for the same set of data. In this example, the histogram is vertical instead of .c) In a box and whisker plot, one whisker represents about _____ % of the data. Solution : a) The interquartile range of a data is the difference of the upper quartile and the lower quartile. b) In a box and whisker plot, the entire box represents about 50% of the data. c) In a box and whisker plot, one whisker represents about 25 % of the data.Students use informal language to describe the shape, center, and variability of a distribution based on a dot plot, histogram, or box plot. Students recognize that a first step in interpreting data is making sense of the context.
Find step-by-step Precalculus solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: These box plots show the basketball scores for two teams: Bulldogs: $\text{Min}=55,Q_1=70,Q_2=80,Q_3=90,\text{Max}=105$ Wolverines: $\text{Min}=35,Q_1=55,Q_2=80,Q_3=85,\text{Max}=96$ Compare the shapes of the box plots. .

3 16 sheet metal price

$23.99
shape of distribution box plots|explain box plot with example