box plot directly comparing the distributions of each subject Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the . One of the most charming Flea Market gardening-style containers is an old toolbox, either metal or wood. Here are two How To planting projects using a metal and wooden toolboxes and a gallery of our best examples. Toolboxes are always on my mental shopping list.
0 · symmetrical box plot
1 · symmetrical box distribution
2 · how to find box distribution
3 · box vs whisker plot
4 · box plots explained
5 · box plot calculation
6 · box plot anatomy
7 · box and whisker plot example
It is normally meant as a star of the devil or a wicken's house. They are growing in popularity but most people do not know that it is part of a rare but growing club.
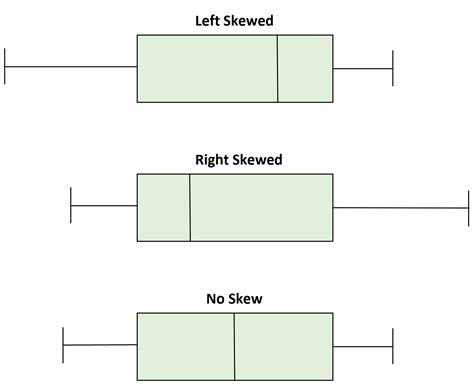
When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare .
Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the .In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize .
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
Box plots are particularly useful for data analysis when comparing two or more data sets; it is easy to make visual comparisons of average (median) and spread (range and interquartile range). When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median .Box plots offer a quick and informative way to: Visualize spread: Show how data varies within a set. Identify key values: See the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. Compare datasets: Easily compare distributions side-by-side. How .In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
A box plot is constructed from five values: the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value. We use these values to compare how close other data values are to them. To construct a . When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
symmetrical box plot
symmetrical box distribution
cnc machining center price
Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From this, the spread and skew of the data can also be seen.In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable. In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
Box plots are particularly useful for data analysis when comparing two or more data sets; it is easy to make visual comparisons of average (median) and spread (range and interquartile range). When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?Box plots offer a quick and informative way to: Visualize spread: Show how data varies within a set. Identify key values: See the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. Compare datasets: Easily compare distributions side-by-side. How can this resource help? This resource provides a clear explanation and examples: Explanation: Defines box .
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment. A box plot is constructed from five values: the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value. We use these values to compare how close other data values are to them. To construct a box plot, use a horizontal or vertical number line and a rectangular box.
When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.Box plots are a useful way to compare two or more sets of data visually. In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From this, the spread and skew of the data can also be seen.In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.Box plots are particularly useful for data analysis when comparing two or more data sets; it is easy to make visual comparisons of average (median) and spread (range and interquartile range). When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?Box plots offer a quick and informative way to: Visualize spread: Show how data varies within a set. Identify key values: See the median, quartiles, and potential outliers. Compare datasets: Easily compare distributions side-by-side. How can this resource help? This resource provides a clear explanation and examples: Explanation: Defines box .
In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment.
cnc machining certification san diego
how to find box distribution
Machines achieve several manufacturing operations, and might be either manual (operated by a machinist) or equipped with Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology. Apart from machinery, a machine shop might also involve .
box plot directly comparing the distributions of each subject|box plots explained